Efficiency, Equity, and Concentration of Power A monopoly firm determines its output by setting marginal cost equal to marginal revenue It then charges the price at which it can sell that output, a price determined by the demand curve That price exceeds marginal revenue;Economic efficiency is maximized when price (P) from selling the product is equal to marginal cost (MC) of producing it When price (P) is equal to marginal revenue (MR), both profit and efficiency are maximized Whether price is equal to marginal revenue or not depends on how pricing is doneEarn a 5 on the AP Micro Exam!

The Impact Of Covid 19 On Potential Output In The Euro Area
Economically efficient output level
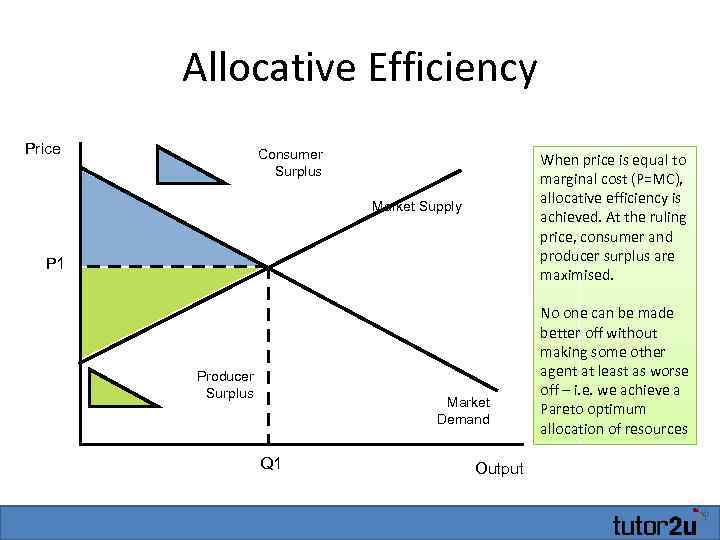
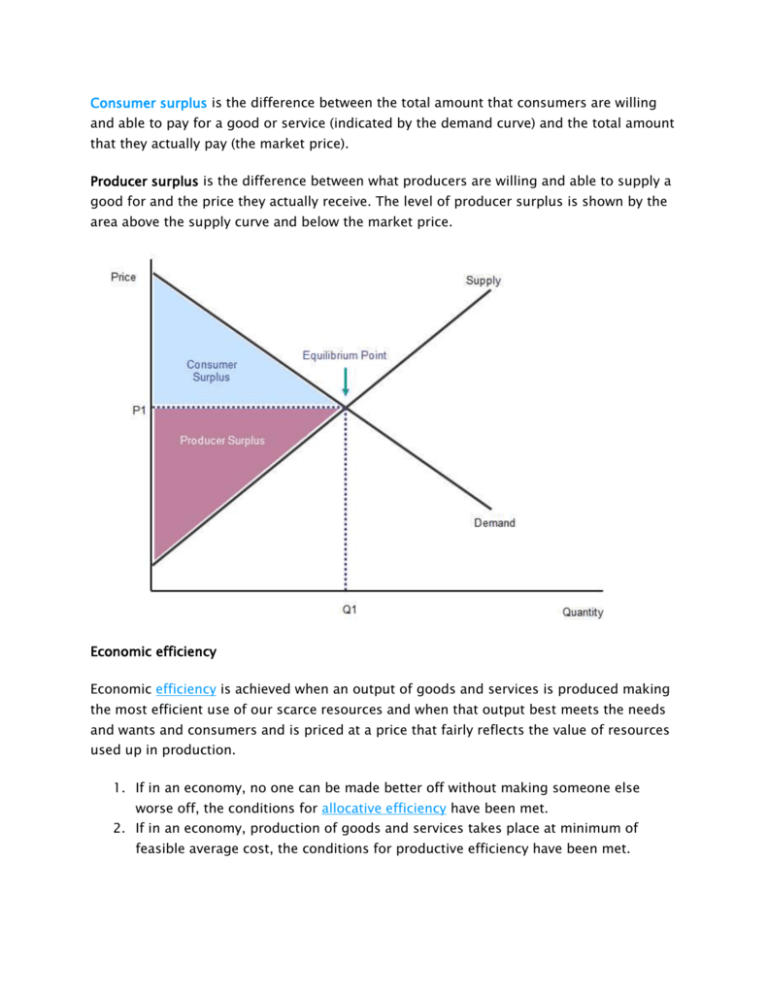
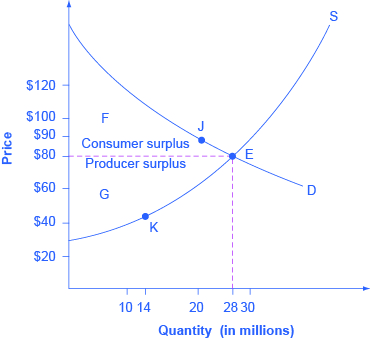
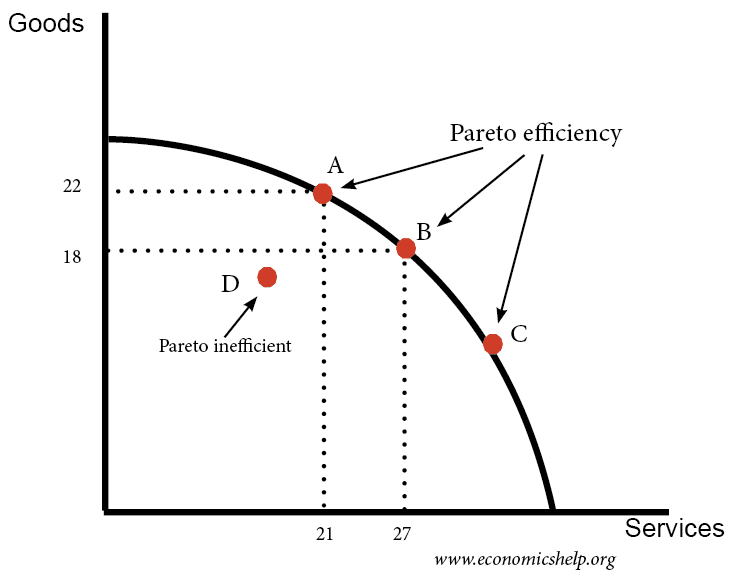
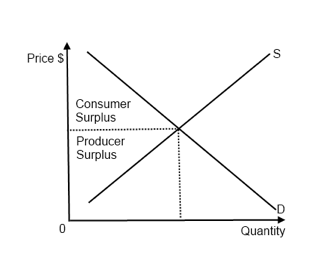
Economically efficient output level-There is a negative externality associated with the production of the good depicted The socially efficient level of output is 23 Refer to the above supply and demand graph In the graph, line S1 is the current supply of this product, while line S1isWhat is the economically efficient output level?, At the efficient level of output, it is impossible to produce greater consumer surplus without reducing producer surplus, and it is impossible to produce greater producer surplus without reducing consumer surplus This efficient level is the market equilibrium!
/MinimumEfficientScaleMES2-c9372fffba0a4a1ab4ab0175600afdb6.png)



Minimum Efficient Scale Mes Definition
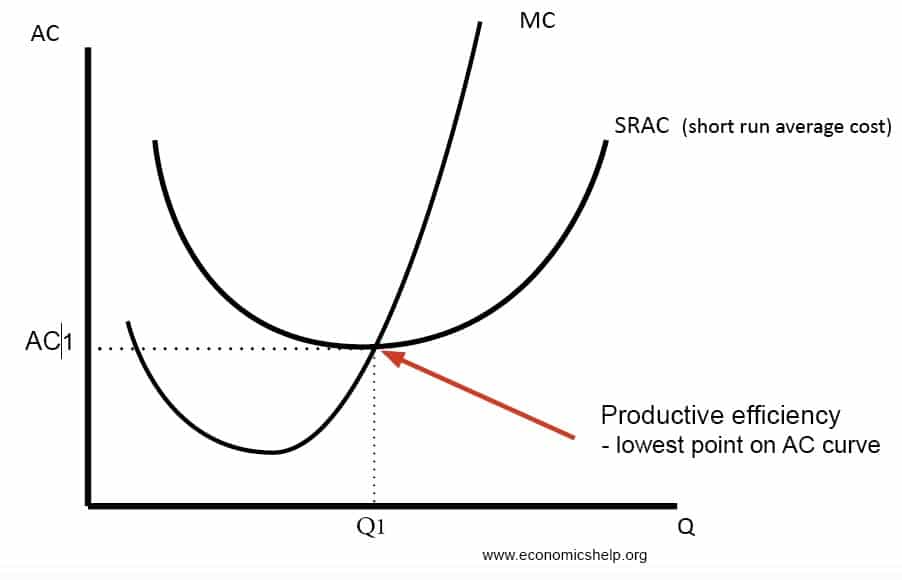
Asked in Economics by Chunlee A) Q2, P2 B) Q2, P3 C) Q3, P2 D) Q4, P1 principlesofeconomics;This is the point where average costs are minimum The efficient output level is Q* and average cost is AC* At any other point (like E1) average cost is higher (AC1 >4 To reach an economically efficient output level, the size of an excise tax imposed on a firm generating a negative externality should be a the firm's marginal cost b the social marginal cost c the difference between the social marginal cost and the firm's marginal cost d the sum of the social marginal cost and the firm's marginal cost 5
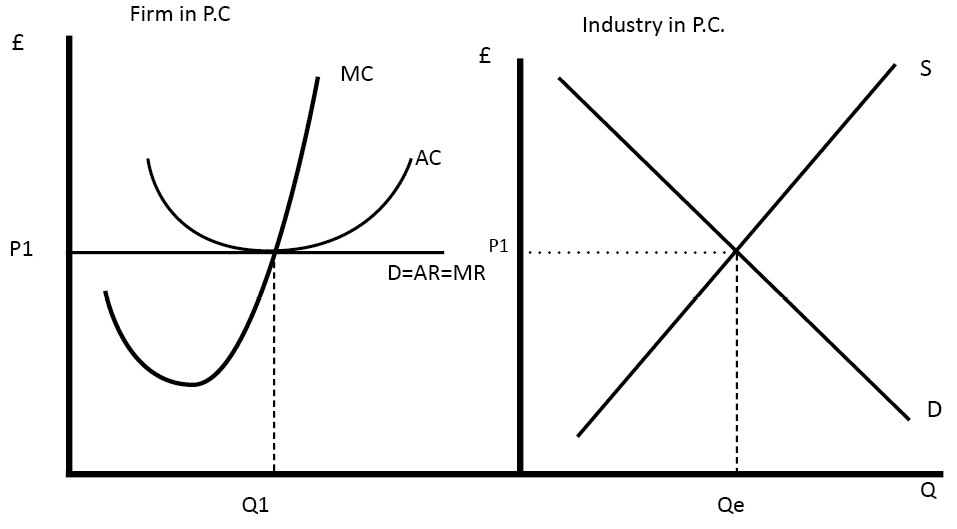
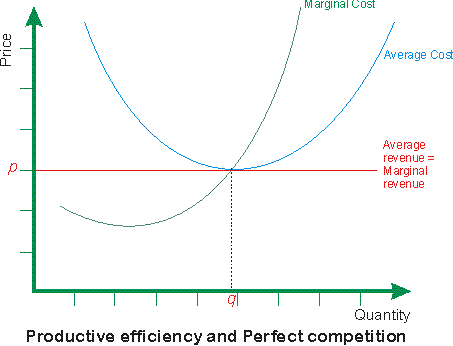
In microeconomics, economic efficiency is, roughly speaking, a situation in which nothing can be improved without something else being hurt Depending on the context, it is usually one of the following two related concepts Allocative or Pareto efficiency any changes made to assist one person would harm another Productive efficiency no additional output of one good can beSpecialisation and managerial economies of scale (expert engineers and pilots)In this video, see how markets might produce an
Econ Exam II more than the economically efficient output level Refer to Figure 48 Suppose the current market equilibrium output of Q1 is not the efficient output because of an externality The economically efficient output is Q2 In that case, the diagram showsConsumer preferences An economy could be productively efficient but produce goods people don't need this would be allocative inefficient Allocative efficiency occurs when the price of the good = the MC of production A more precise definition of allocative efficiency isA) more than the economically efficient output level B) less than the economically efficient output level C) products at a low opportunity cost D) products at a high opportunity cost 10 If the social benefit of consuming a good or a service exceeds the private benefit A) a negative externality exists B) the market achieves economic



2




Hubbard Micro6e Ppt Ch04
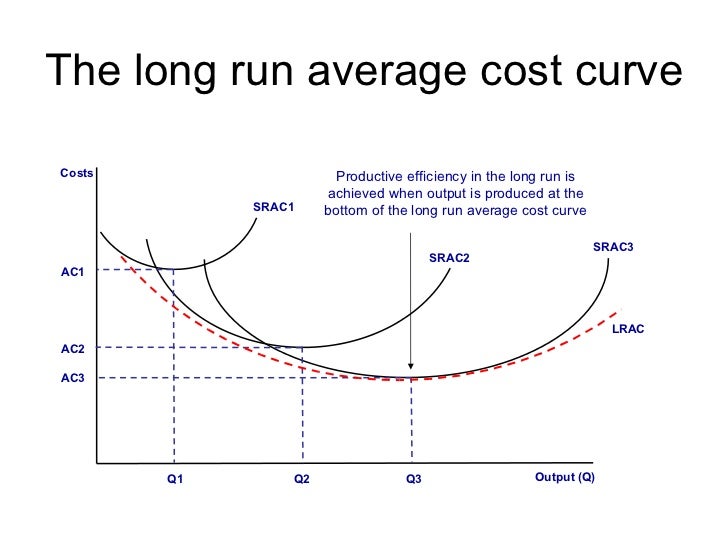
Productive efficiency is satisfied when a firm can't possibly produce another unit of output without increasing proportionately more the quantity of inputs needed to produce that unit of output It's met when the firm is producing at the minimum of the average cost curve, where marginal cost (MC) equals average total cost (ATC) (Sometimes youW Whittaker, in Encyclopedia of Health Economics, 14 A Production Possibility Frontier Approach to Resource Allocation Economic efficiency consists of two types of efficiency, allocative and technical efficiency Allocative efficiency concerns producing the maximum output subject to inputs, ie, it is not possible to increase output simply by reallocating resources, and it isAn economically efficient method of production produces a given level of output at the lowest possible cost




Economies Of Scale Definition Types Effects Of Economies Of Scale
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_INV_final_Allocational_Efficiency_Jan_2021-012-8e1bff8c4ccd4e36a7d14530238d4ed0.jpg)



Allocational Efficiency Definition
When this happens, the equilibrium output level will move closer to the allocatively efficient output level resulting in a reduction in allocative inefficiency Benefits and Limitations of Education Using education to correct the market failure of healthcare has its benefits and limitationsQuestion 16 Marks 1 An economically efficient output level is achieved when Choose one answer a the marginal benefit of the last unit produced is less than the marginal cost of producing that unit b the marginal benefit of the last unit produced equals the marginal cost of producing that unit cAn overview of all 18 Microeconomics Graphs you must learn before test day Key parts of all graphs are shown and there is a PDF cheat sheet to download Make sure you know these Micro Graphs before your next exam Study &



The Model Of Perfect Competition A 2 Microeconomics



Solved Price Of Vaccinations S P2 Bic A P D D2 D 0 0 No Chegg Com
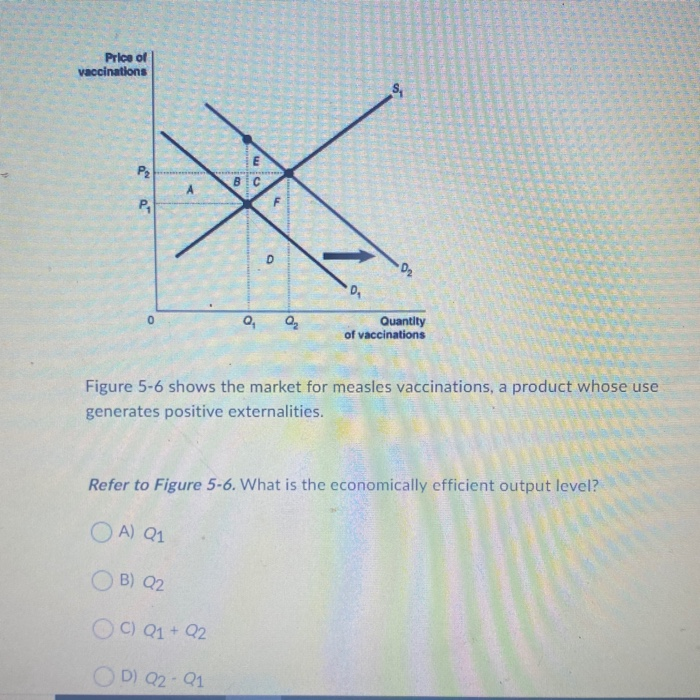
O A because Erickson Power will earn zero profit O B because at the economically efficient output level, the marginal cost of producing the last unit sold exceeds the consumers' marginal value for that last unit O C because there is insufficient demand at that output level a1 Q2 0 D because Erickson Power will sustain MR persistent losses0 Answers 0 votes answered by Inno78Chapter 6 Economic Efficiency 6 Analyze the economic consequences of taxes NOTES 1 Concept of economic efficiency (a) An allocation of resources (quantity) is economically efficient where no reallocation can make one person (human being or business) better off without making another worse off i



Lecture 31 Notes




Efficiency Types Economics Online Economics Online
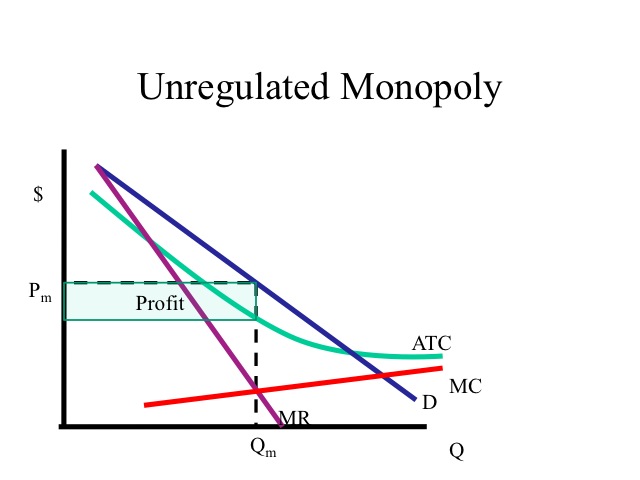
A monopoly is an imperfect market that restricts output in an attempt to maximize profit Market failure in a monopoly can occur because not enough of the good is made available and/or the price of the good is too high deadweight loss A loss of economic efficiency that can occur when equilibrium for a good or service is not Pareto optimalIt therefore exceeds marginal cost as wellNow consider point Y where output quantity has increased to million With this new production level is associated a new isocost curve with total cost at C 2 Finally, point Z indicates that for an output quantity of 30 million the total cost is C 3 From




A Graphical Illustration Of The Comparison Among Agronomic Efficiency Download Scientific Diagram
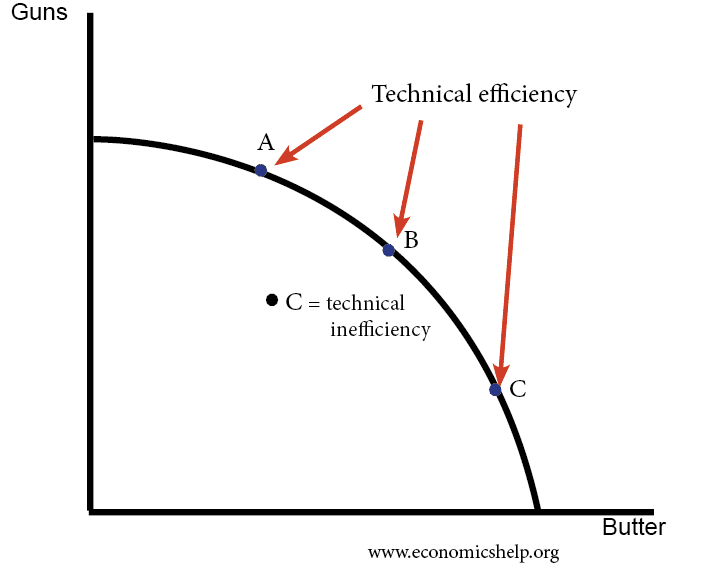



Technical Efficiency Definition Economics Help
– FOORQUIZ Refer to Table 154In that case, the level of aggregate demand in the economy is above the 45degree line, indicating that the level of aggregate expenditure in the economy is greater than the level of output When the level of aggregate demand has emptied the store shelves, it cannot be sustained, either Firms will respond by increasing their level of productionOutput is at its equilibrium when quantity of output produced (AS) is equal to quantity demanded (AD) The economy is in equilibrium when aggregate demand represented by C I is equal to total output Under short run fixed price, equilibrium level of output is determined solely by level of



Economic Efficiency Economics Help




Econowaugh Ap 11 02 14
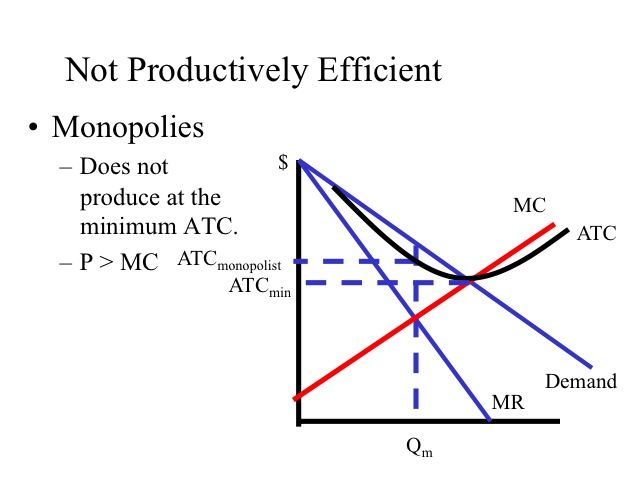
To reach an economically efficient output level, the size of an excise tax imposed on a firm generating negative externality should be the difference between the social marginal cost and the firm's marginal cost Normally the Government applies this rule to make sure that even if a particular company faces a loss in the following year or month even then it can be able to pay the amountThis is illustrated in Figure 125 of the text, reproduced as Figure 1 below The Paretoefficient output of bananas is 38,000 tonnes, where the marginal social cost is equal to the price ($400) The tax is equal to the difference between the marginal social cost and the marginal private cost at this level of output, which is $100AC*) If a firm produces less than Q* it is productively inefficient This concept applies to an output level that exceeds Q* also At E2 average cost is AC2 while output is Q2




Productive Efficiency Wikipedia



2
Economy results in a payment to the inputs that produced it in the form of rent, wages, interest, or dividends Y (playing the dual role of output and income) is the endogenous variable in the model that measures the dollar flow during a specific time period (2) Output is demanded by three types of agents consumers, firms, and the governmentProductive machinery spread over a large number of output ie passengers) One type of plane used >The marginal cost rows have been placed between two output levels because marginal cost is the perunit cost of increasing production from one level to the next level In this example, $425 is placed between 1,000 and 2,000 pens The profit (Column I) at a given production level equals the total revenue (Column C) minus the total cost
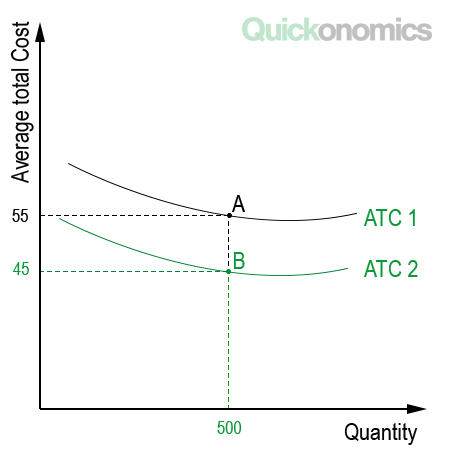



Five Types Of Economic Efficiency Quickonomics



File
What is the economically efficient output level and what is the price at that level?Determination of Economic Equilibrium Level of Output!FIGURE 1 FACETS OF "ECONOMIC EFFICIENCY" IN AN ECONOMY Efficiency in production requires a) That available resources are fully used (which means among other things that en economic with involuntary unemployment is ipso facto inefficient) b) Real resources are used so as to maximize the total social value of the output to be had from




Welfare Economics Wikipedia



Econ 150 Microeconomics
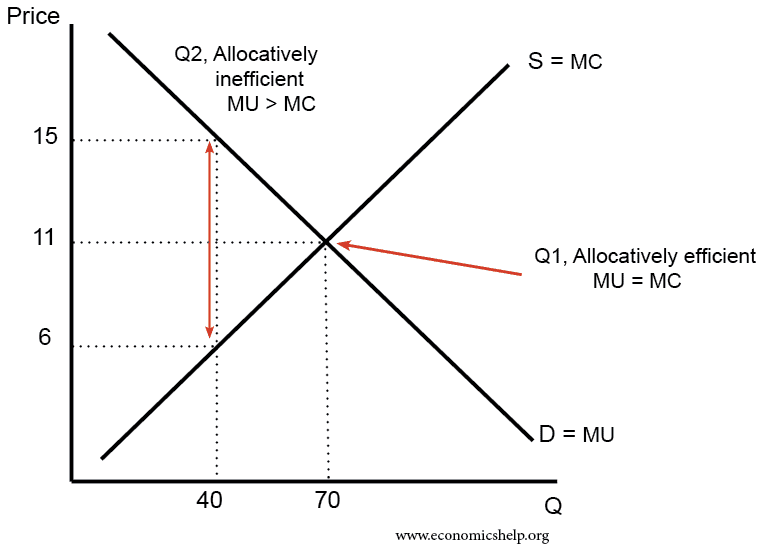
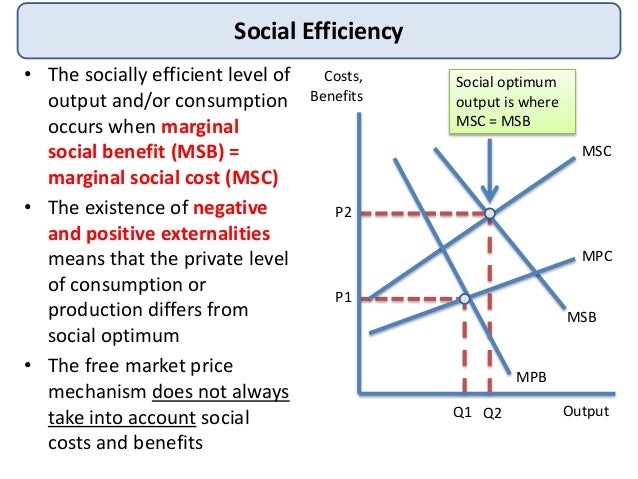
Fuel efficiency of Boeing jets, checkin machines >The concept of dynamic efficiency is commonly associated with the Austrian Economist Joseph Schumpeter and means technological progressiveness and innovation Neoclassical economic theory suggests that when existing firms in an industry, the incumbents, are highly protected by barriers to entry they will tend to be inefficientSchumpeter argued that this is not necessarily the– the most efficient output level for any good or service is attained, where marginal benefit equals marginal cost – of the goods and services satisfying these two costbenefit tests, those with the highest net benefits are included in the economically efficient set •




Ppt Externalities Environmental Policy And Public Goods Powerpoint Presentation Id




Equilibrium Allocative Efficiency And Total Surplus Video Khan Academy
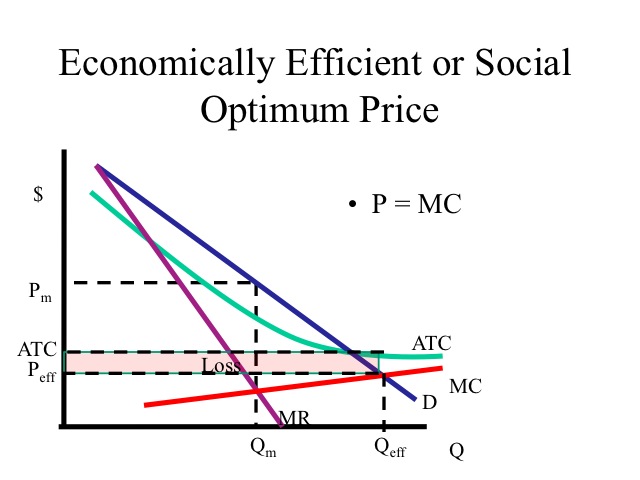
The economic profit is the difference between TR and TC We denote the economic profit by π Then, $$\pi= TRTC$$ Optimal Price and Output in Oligopoly Markets The firm will maximize its profit when the level of output is such that, the marginal revenue equals marginal cost In other words, it will produce the quantity such that MR=MCIdeally, output should expand to a level where P=MC, but this will occur only under pure competitive conditions where P = MR Productive efficiency is not achieved because the firms' output is less than the output at which average total cost is minimumThus, even regulation of monopoly through average cost pricing leads to the expansion in output by the monopolist to OQ 1 level and thereby causes expansion of output towards economically more efficient output (the consumer's surplus or welfare will increase by




Organizing Production This Lecture Explains The Role Of




Micro Exam Four Flashcards Quizlet
Transcript If all costs and benefits are captured by the supply and demand curves, then the market outcome is a quantity where marginal social costs equals marginal social benefit But what if they don't?A key point to understand is the idea that economic efficiency occurs when the cost of producing a given output is as low as possible There's a hidden assumption here, and that is the assumption that all else being equalA change that lowers the quality of the good while at the same time lowers the cost of production does not increase economic efficiencyWhat is the economically efficient output level?



Econ 150 Microeconomics




Answers To Sample Long Free Response Questions
The economically efficient or social optimum price would occur where price equals marginal cost, making the industry allocatively efficient However, since the average total cost is declining in the region of demand, and marginal cost intersects average cost at the minimum, marginal cost will be below the average cost in the relevant range ofWhen one person gets more of something than another, it isn't economically efficient Learn the definition of economic efficiency,Technical economies of scale (more efficient &



1




Solved 43 To Reach An Economically Efficient Output Level Chegg Com
To reach an economically efficient output level, the size of an excise tax imposed on a firm generating a negative externality should be a) the firm's marginal cost b) the social marginal costEconomics questions and answers When a negative externality exists, the private market produces a products at a low opportunity cost b less than the economically efficient output level c products at a high opportunity cost dKey Points Economic efficiency is the idea that it is impossible to improve the situation of one party without imposing a cost on another If a situation is economically inefficient, it becomes possible to benefit at least one party without imposing costs on others Consumer surplus is the gap between the price that consumers are willing to
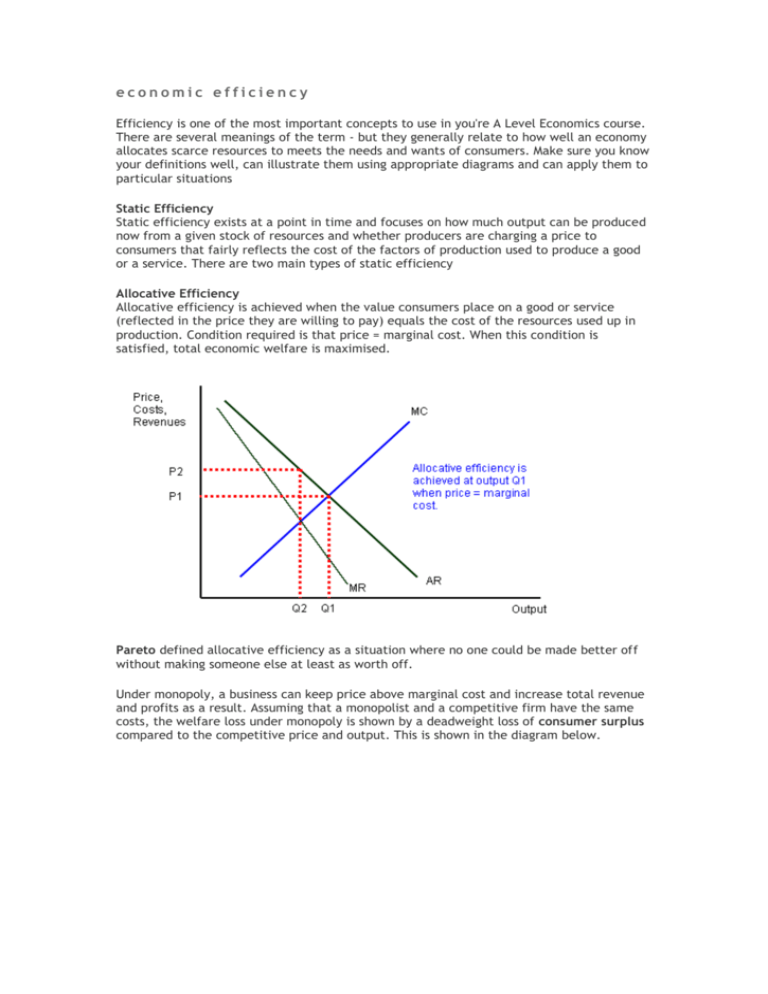



Economic Efficiency




Allocative Productive Efficiency Ppt Download
1) An economically efficient output level is achieved when A) the marginal benefit of the last unit produced equals the marginal cost of producing that unit B) the marginal benefit of the last unit produced is greater than the marginal cost of producing that unit



Monopolistic Competition Overview How It Works Limitations




Allocative Efficiency Definition Example And Graph Boycewire



Economic Efficiency



Economic Efficiency



Economic Efficiency Article Khan Academy



1



2



Econ 150 Microeconomics



Allocative Efficiency Economics Help




Chapter Organizing Production 9 After Studying This Chapter




Negative Externalities Third Party Costs Economics Online Economics Online



Economic Efficiency



Economic Efficiency Economics Help



Economic Efficiency Economics Help




7 Ir Foster 27 The Figure Above Shows The Market Demand And Cost Curves Facing Course Hero




R Foste 4 10 The Figure Below Reflects The Cost And Revenue Structure For A Course Hero




Revision Guru



Ib Economics Notes 1 6 Market Efficiency



Economic Efficiency Market Failure



Economic Efficiency In Perfect Competition And Monopoly
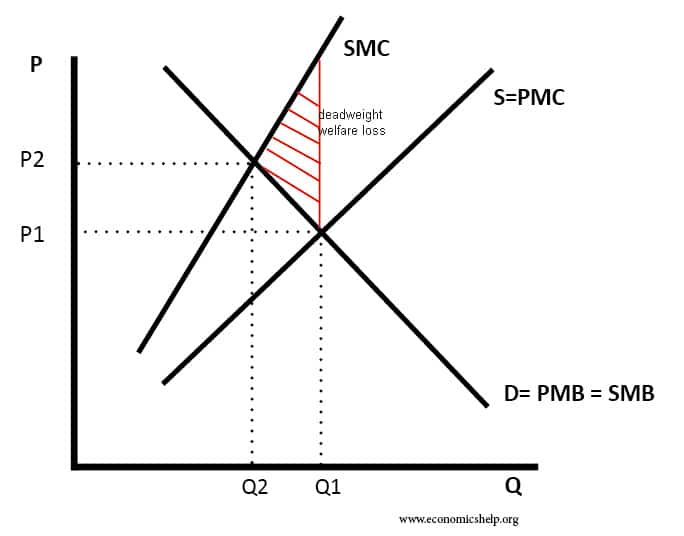



Social Efficiency Economics Help
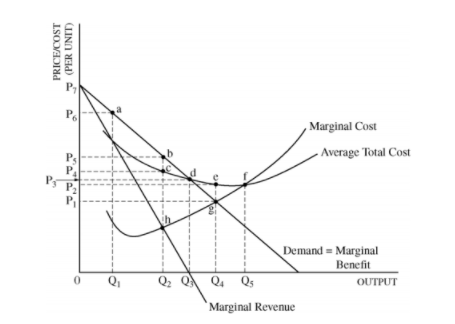



Solved D Suppose The Firm Produces At The Allocatively Chegg Com
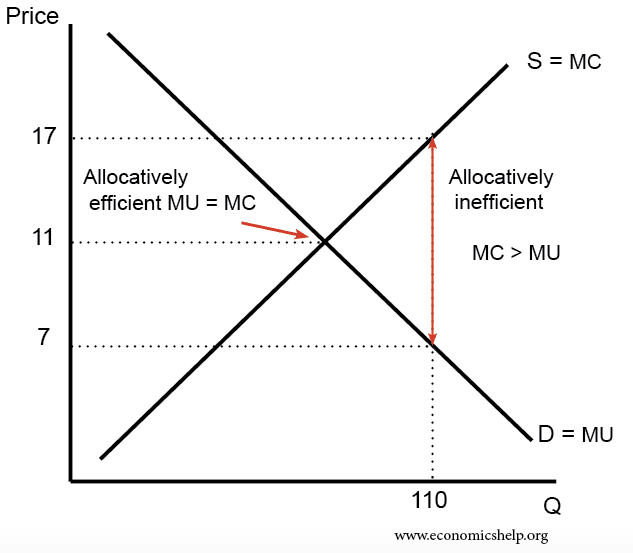



Allocative Efficiency Economics Help
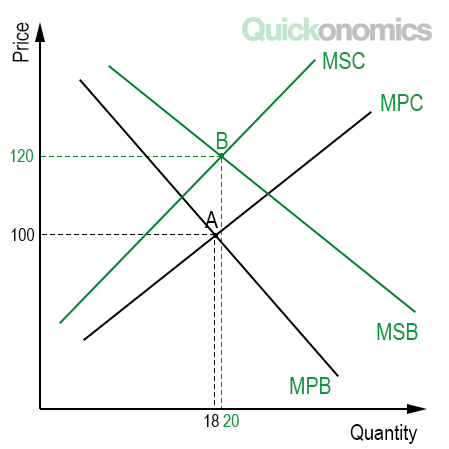



Five Types Of Economic Efficiency Quickonomics
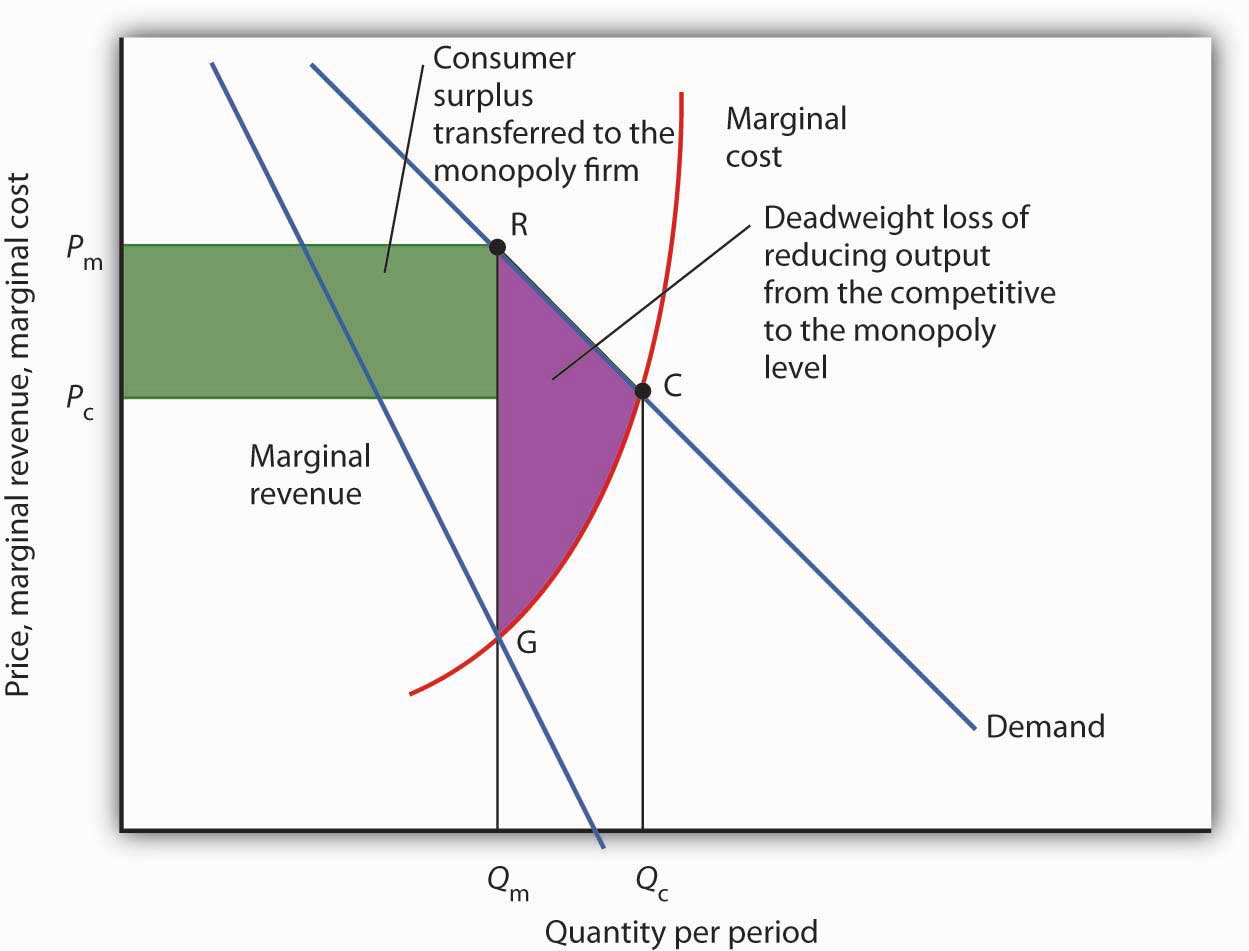



Reading Monopolies And Deadweight Loss Microeconomics
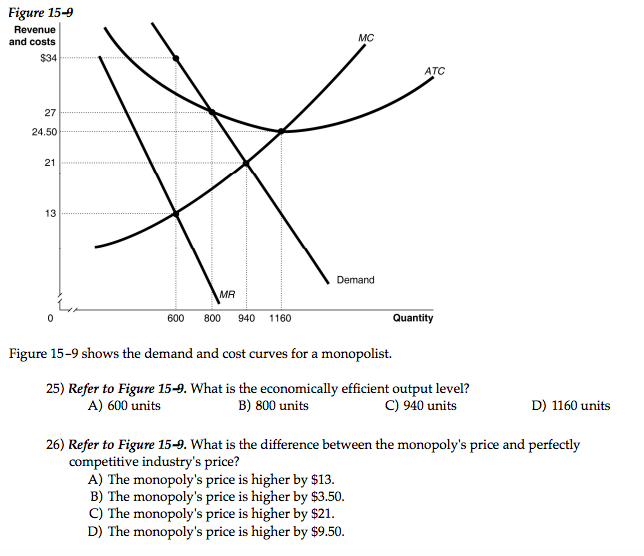



Solved Figure 15 9 Revenue Mc And Costs 34 Atc 27 24 50 21 Chegg Com



Duopoly Cournot Nash Equiibrium




Demand Supply And The Market Process Ppt Download




Which Level Indicates The Point Of Maximum Economic Efficiency A Lowest Point On Ac Curve B Lowest Point On Avc Curve C Lowest Point On Mc Curve D None Of These




The Impact Of Covid 19 On Potential Output In The Euro Area




Chapter 18 Graphs Flashcards Quizlet




Final Flashcards Quizlet




To Reach An Economically Efficient Output Level The Size Of An Excise Tax Imposed On A Firm Generating A Negative Externality Should Be A The Firm S Marginal Cost B The Social Marginal




4 Economic Efficiency Government Price Setting And Taxes Chapter Economic Efficiency Government Price Setting And Taxes Tenants In Rent Controlled Ppt Video Online Download




Natural Monopolies Economics Online Economics Online




Comparison And Analysis Of The 4 Market Structures
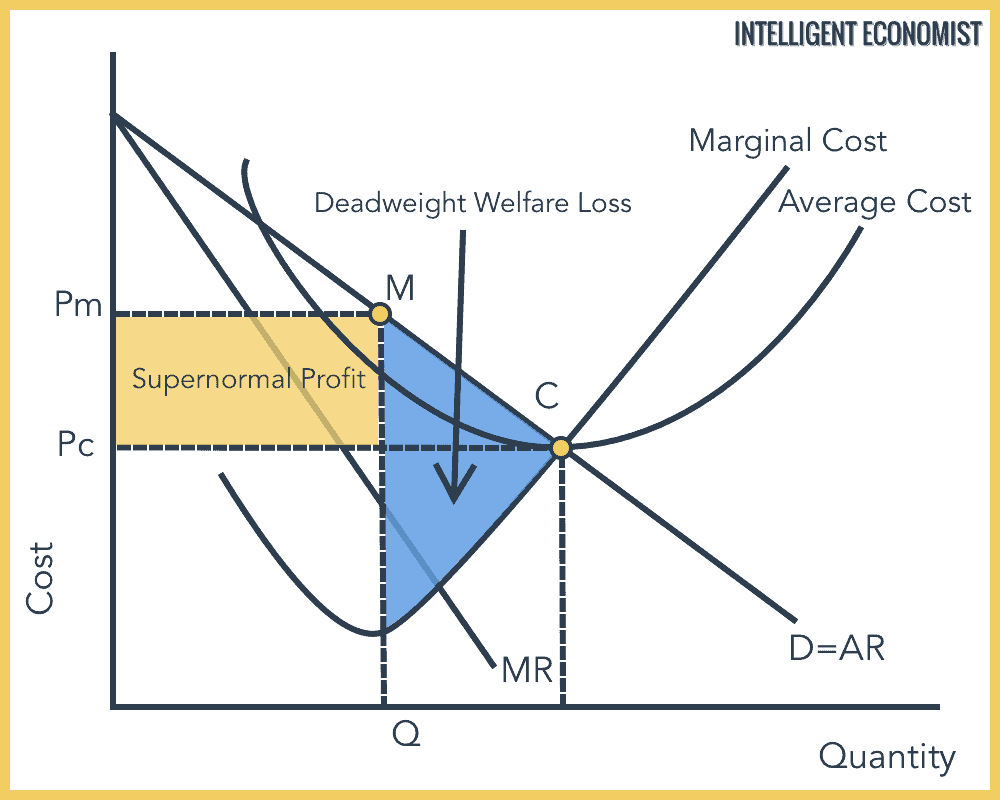



Allocative Efficiency Intelligent Economist
/MinimumEfficientScaleMES2-c9372fffba0a4a1ab4ab0175600afdb6.png)



Minimum Efficient Scale Mes Definition




Consumer Producer Surplus Pages Mr Henry Ap Economics Ppt Download



Lecture 28 Notes




Different Types Of Efficiencies Public Economics




Efficiency Types Economics Online Economics Online




The Inefficiency Of Monopoly Microeconomics
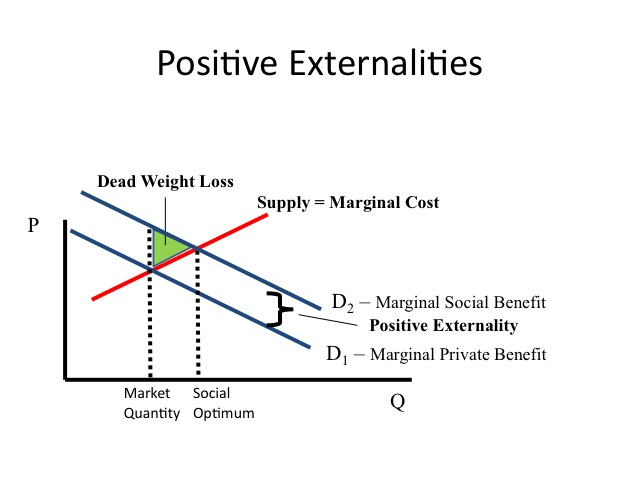



Econ 150 Microeconomics




Macroeconomics Econ 2302 Fall Ppt Download



2
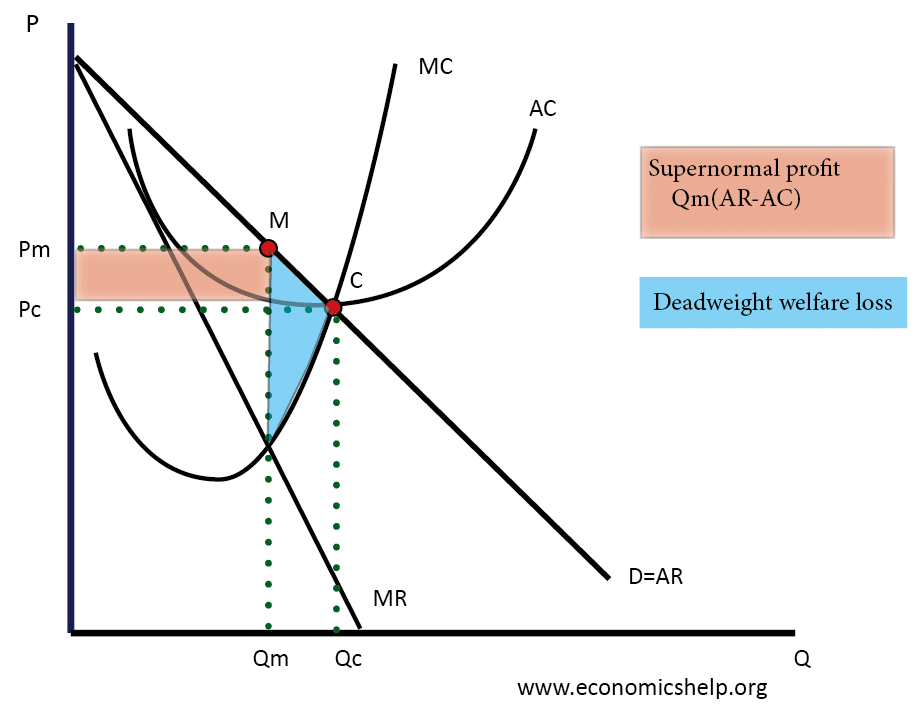



Allocative Efficiency Economics Help



Supply Demand And Economic Efficiency



1




About Here 4 Results And Discussion Download Table




Ch 10 Organizing Production Definition Of A Firm
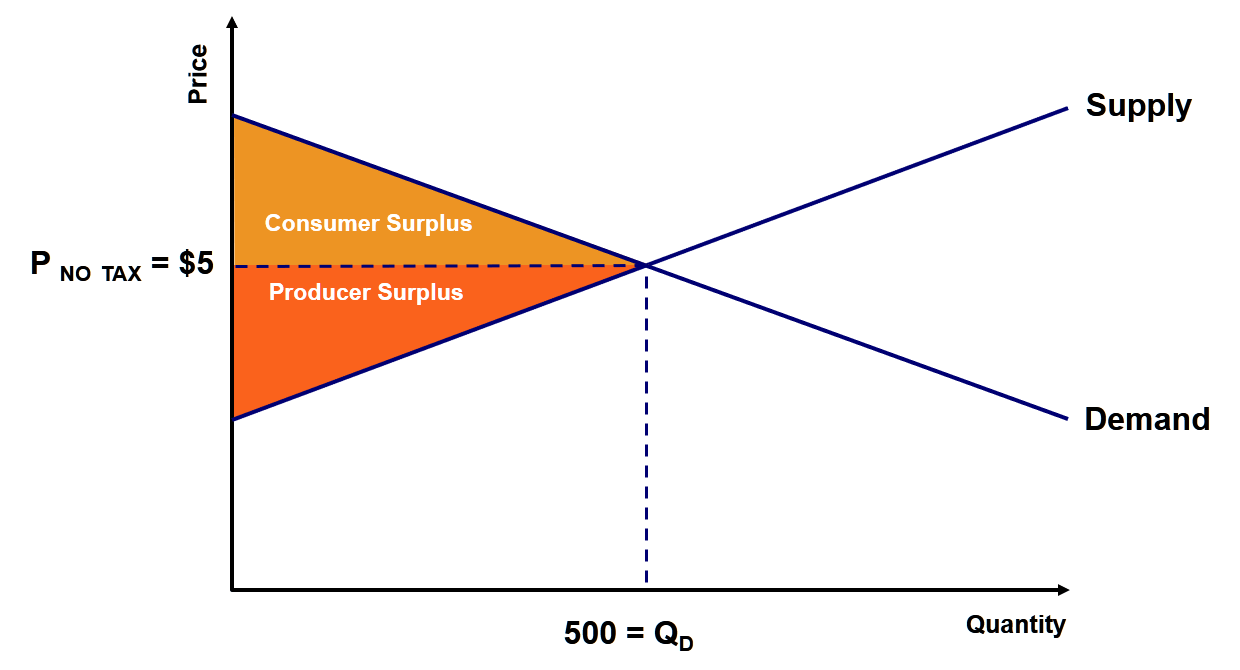



Deadweight Loss Examples How To Calculate Deadweight Loss



Supply Demand And Economic Efficiency




Bec Managerial Economics Theory Of Production Cost
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Production_Possibility_Frontier_PPF_Apr_2020-01-b1778ce20e204b20bf6b9cf2a437c42e.jpg)



Production Possibility Frontier Ppf Definition
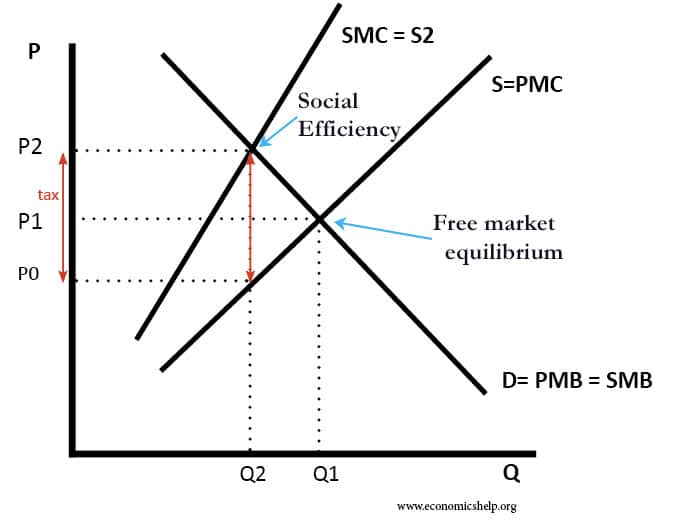



Social Efficiency Economics Help



3
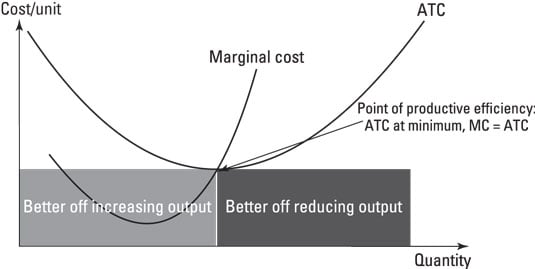



Productive Efficiency Producing For The Lowest Possible Cost Dummies



Solved 4 The Graph Below Shows The Demand And Cost Curves For A Monopolist Revenue And Costs 34 27 21 13 L Mr 0 600 800 940 1 Course Hero




Long Run Price And Output Under Perfect Competition Sentinel007 S Blog
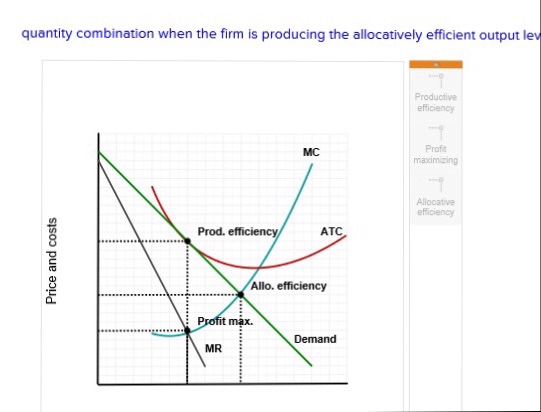



Solved Consider The Diagram Below Depicting The Demand And Chegg Com
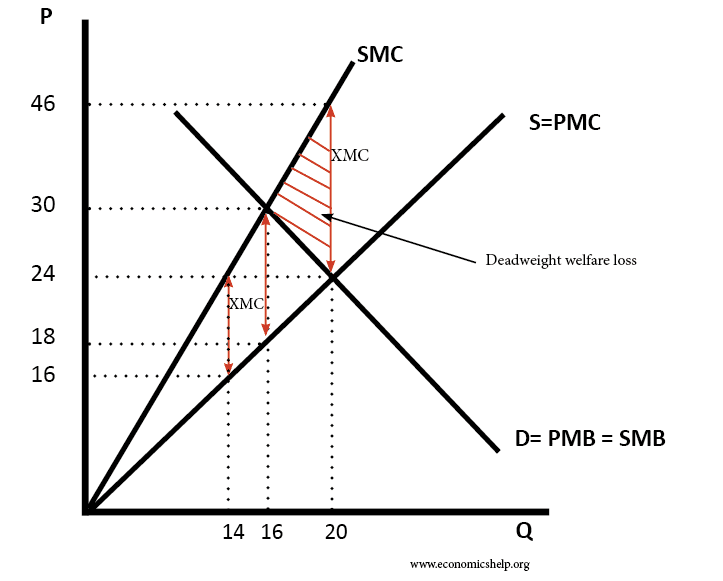



Economic Efficiency Economics Help



2




Micro Final Flashcards Quizlet
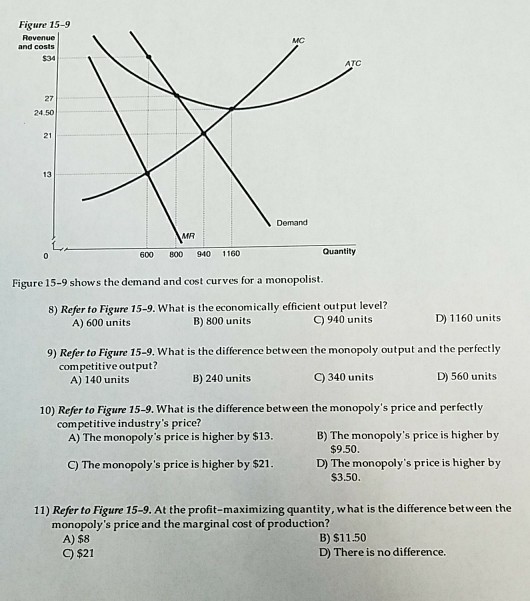



Solved Figure 15 9 Revenue Mc 34 Atc 27 24 50 21 13 Demand Chegg Com
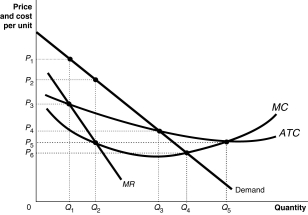



Quiz Figure 10 16
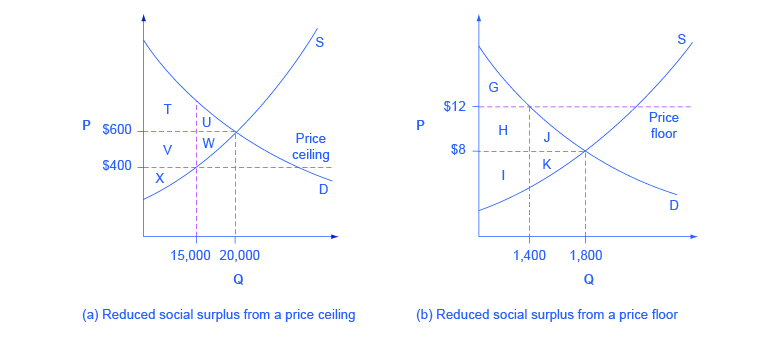



Economic Efficiency Article Khan Academy
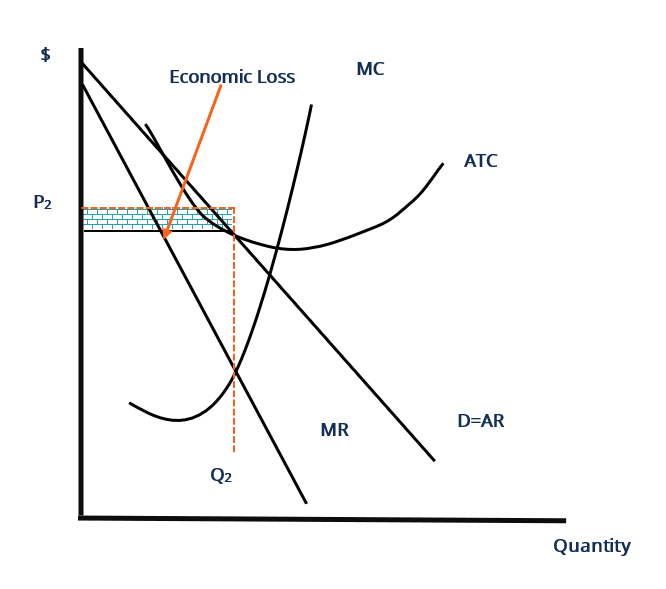



Monopolistic Competition Overview How It Works Limitations




Chapter Twenty Four Monopoly Pure Monopoly U A Monopolized Market Has A Single Seller U The Monopolist S Demand Curve Is The Downward Sloping Market Ppt Download
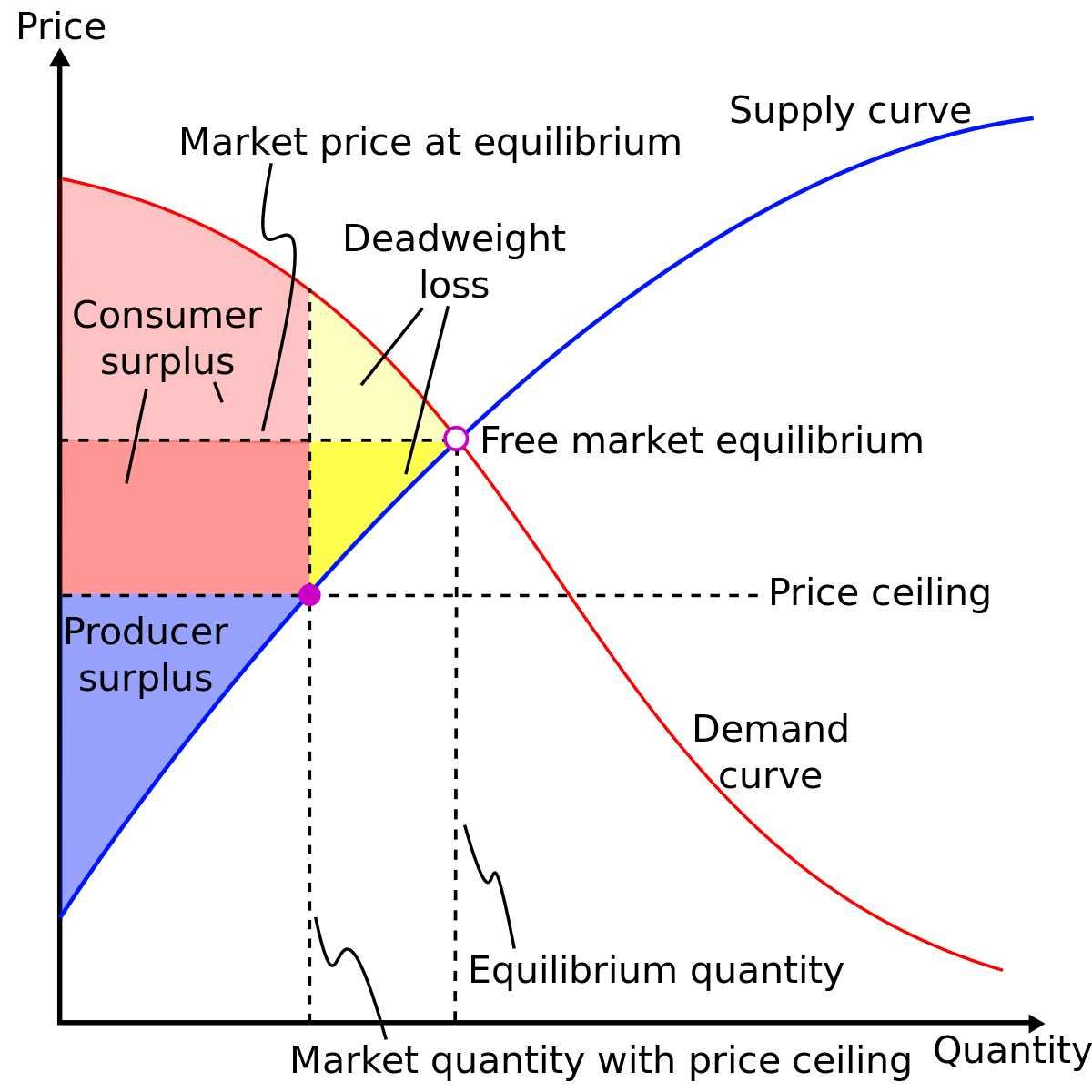



Deadweight Loss Wikipedia
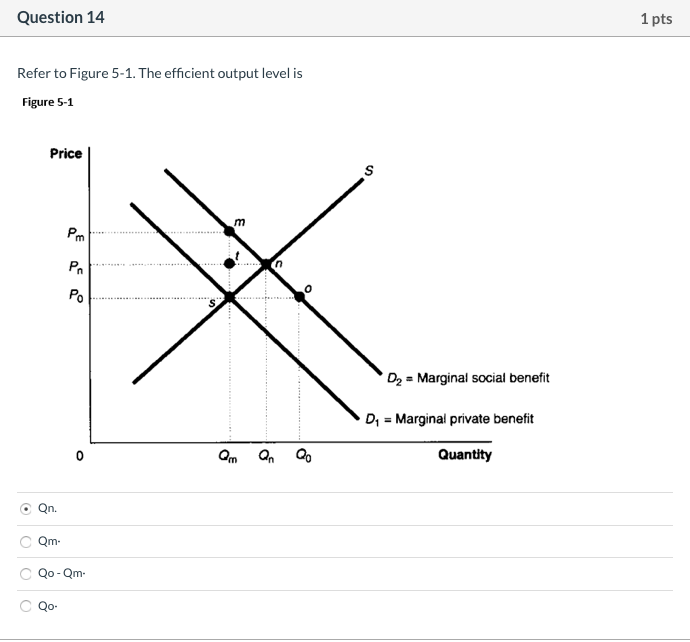



Solved Question 14 1 Pts Refer To Figure 5 1 The Efficient Chegg Com
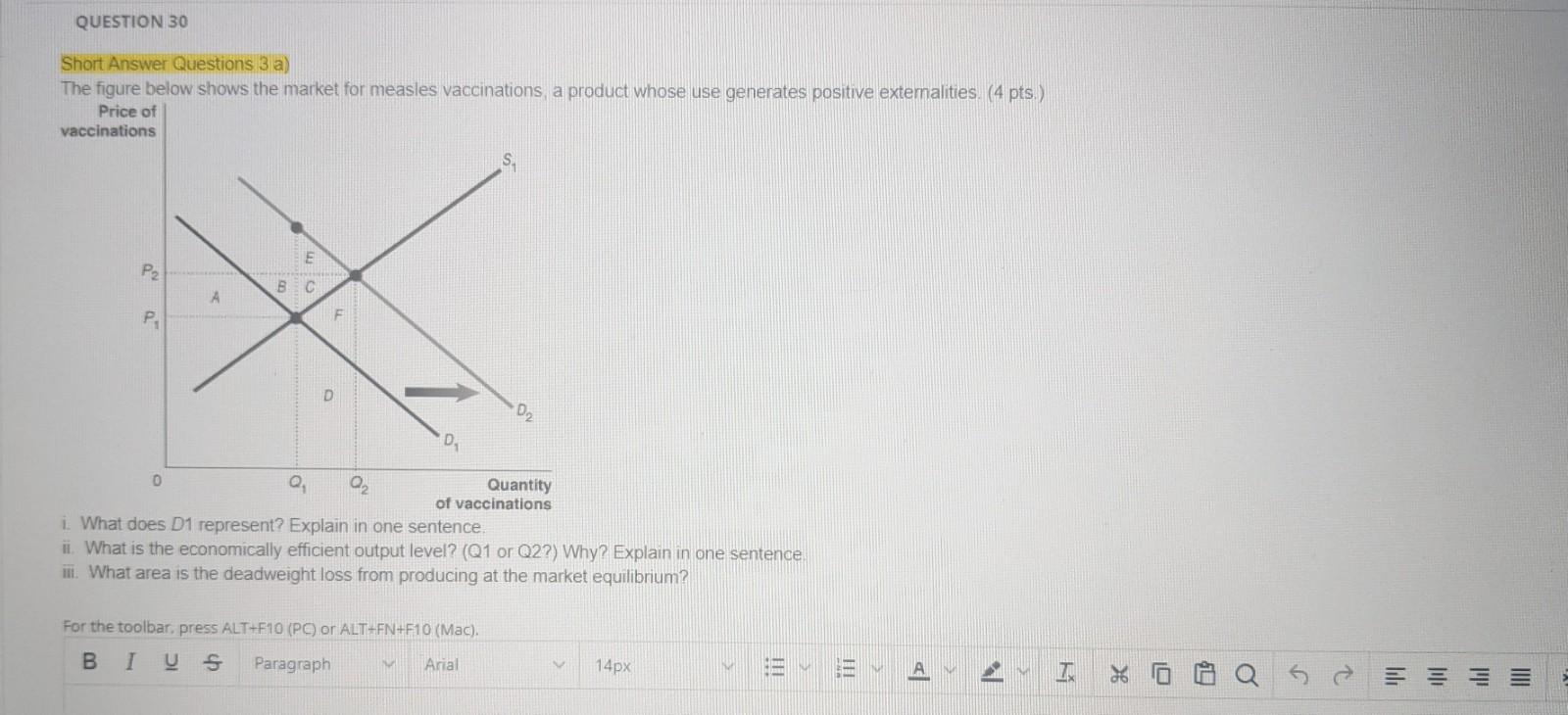



Solved Question 30 Short Answer Questions 3 A The Figure Chegg Com
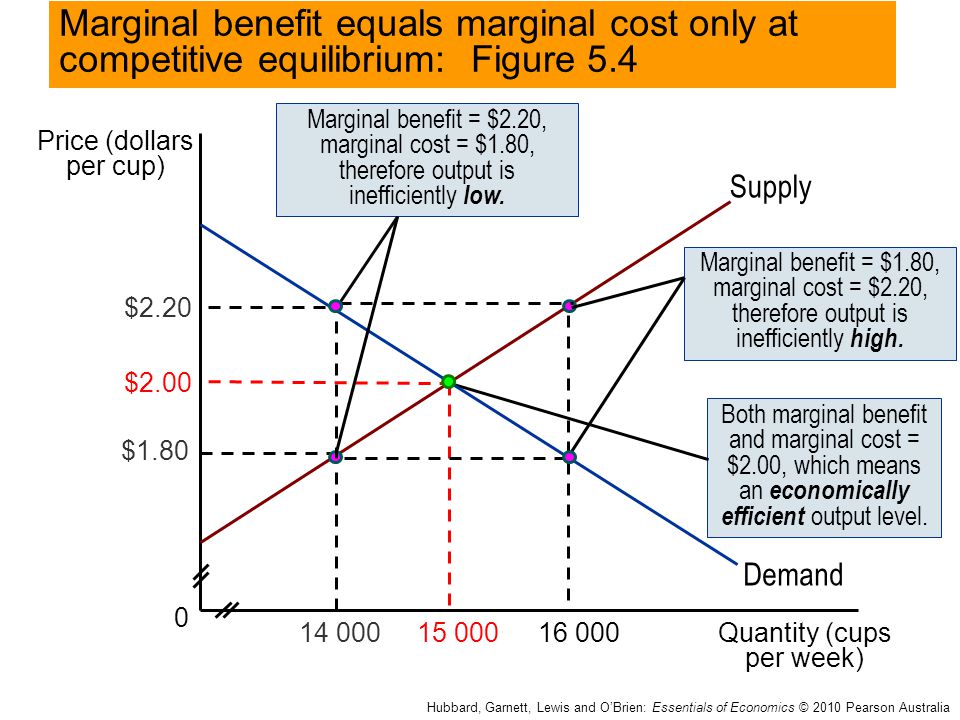



Economic Efficiency And Market Failure Ppt Download



2
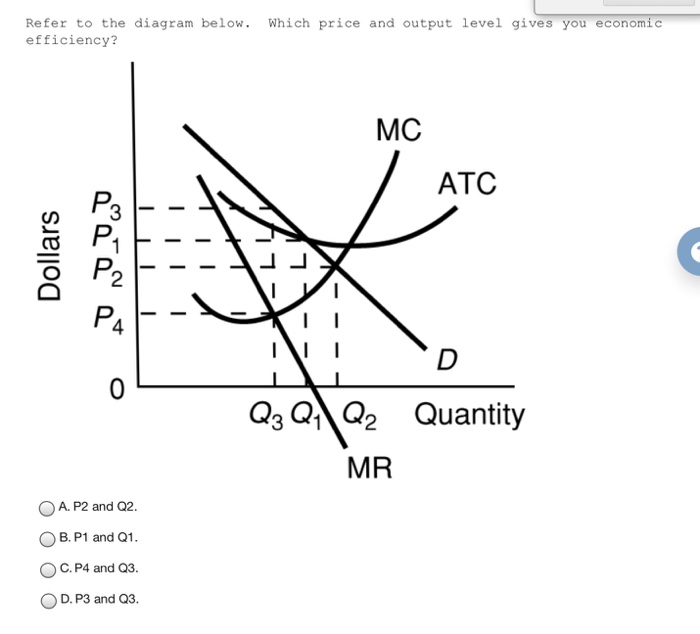



Solved Refer To The Diagram Below Which Price And Output Chegg Com



What Is Economic Efficiency



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿